How to Reduce Your Private Health Insurance Tax Burden
You can minimize your private health insurance tax cost, optimize your tax-deductible premiums, and apply pre-tax salary contributions for insurance premiums under your employer plan. Make sure you are eligible for any tax credits or subsidies and explore salary sacrifice to reduce your taxable income.
Introduction to Private Health Insurance Tax
Private health insurance tax describes the cost or fees individuals incur when they purchase private health insurance policies. Differing from government-run initiatives such as Medicare or Medicaid or private health insurance may have its tax factors. The amounts paid for premiums on private health insurance are deductible on taxes thus lowering one total taxation. The tax status of private health insurance premiums can change. It depends on factors like if the insurance is bought through an employer or individually. It is critical to know these nuances to effectively manage how private health insurance tax can impact your budget.
The private health insurance tax can be affected by subsidies with tax credits and the design of your health insurance plan. An individual will be eligible for subsidies that cut back on premiums which subsequently may decrease taxable income, for other individuals pre-tax dollars paid on premiums will produce varying tax implications. Learning how the tax codes work when it comes to private health insurance will help save money or save money in taxes when the time arrives. Successful tax planning will enable you to make informed choices regarding your healthcare coverage and reduce the private health insurance tax that you pay.
Strategies to Minimize Your Private Health Insurance Tax Burden
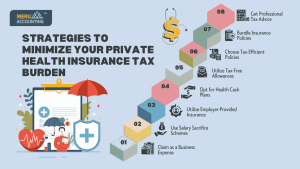
1. Claim as a Business Expense
- Limited companies can deduct health insurance as a business expense.
- Self-employed individuals may qualify for certain tax-efficient options.
- Sole traders and partnerships cannot claim personal health insurance but can explore alternative reliefs.
2. Use Salary Sacrifice Schemes
- Exchange part of your salary for private health insurance benefits.
- Reduces taxable income, lowering income tax and National Insurance contributions.
- Employers must ensure compliance with HMRC regulations.
3. Utilize Employer-Provided Insurance
- Employers providing health insurance classify it as a ‘benefit in kind’ (BIK).
- Employees pay tax on the benefit value, while employers can claim deductions.
- Some healthcare plans qualify for lower tax rates.
4. Opt for Health Cash Plans
- Covers routine medical expenses like dental and optical care.
- Often more affordable with fewer tax implications than full private insurance.
5. Utilize Tax-Free Allowances
- Some health insurance benefits may qualify for tax exemptions.
- Preventive healthcare services like screenings and check-ups may be tax-free.
6. Choose Tax-Efficient Policies
- Certain insurers offer tax-optimized policies.
- Consult a financial advisor to select the best option for tax savings.
7. Bundle Insurance Policies
- Combining health insurance with life or critical illness coverage can be tax-efficient.
- Some bundled policies include tax-deductible elements.
8. Get Professional Tax Advice
- UK tax rules can be complex; expert guidance ensures compliance.
- A tax advisor can help maximize your savings and reduce liabilities.
Maximizing Tax Benefits with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
- Pre Tax Contributions: You may contribute to an HSA to reduce your taxable income which decreases the total health insurance tax you owe. They directly decrease your tax bill because contributions are made using pre-tax dollars.
- Tax-Free Withdrawals: You may withdraw for eligible medical expenses tax-free which can decrease future private health insurance tax liabilities by using your HSA to pay out-of-pocket healthcare expenses.
- Tax Deferred Growth: Tax-deferred accumulation of funds in an HSA allows you to generate interest or investment income without having to pay taxes on it. Future private health insurance tax expenditures associated with rising medical costs may be covered by this accumulation.
- No “Use-It-or-Lose-It” Rule: HSA funds are carried over from year to year which allows you to accumulate savings over time and reduce your long-term health insurance tax burden.
- Long-Term Retirement Benefits: You can withdraw HSA dollars for any reason without penalty subject only to income tax beginning at age 65. This benefit lowers future private health insurance tax burdens as you move into retirement.
Conclusion
At Meru Accounting, we help you make the most of Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) to lower your health insurance tax costs. HSAs let you save money before taxes, grow your savings without taxes, and withdraw funds tax-free for medical expenses. This helps you reduce both your current and future tax burden.
Another benefit of HSAs is that the money stays in your account year after year, so you don’t lose it. You can even use it for retirement without any penalties. By using HSAs wisely, you can manage your health insurance costs better and improve your overall financial health. Meru Accounting can guide you in using HSAs effectively to save on taxes and secure your future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a Health Savings Account (HSA)?
- Ans. An HSA is a tax favored savings account that is used to save for medical expenses. It has tax free contributions with investment growth and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses.
2. How can an HSA lower my private health insurance tax burden?
- Ans. You minimize your taxable income as well as decreasing your total health insurance tax burden by contributing pre tax income to your HSA.
3. Can Meru Accounting help with HSA tax benefits?
- Ans. Yes, Meru Accounting can assist you in maximizing contributions and deductions in your HSA while decreasing your private health insurance tax burden.
4. Are private health insurance premiums deductible?
- Ans. Depending on your circumstances premiums can be tax deductible if you claim your deductions or are self employed. You can as well talk to a tax expert to ensure you qualify.
5. What else can minimize my health insurance tax?
- Ans. You can utilize tax credits and salary sacrifice can minimize your private health insurance tax burden using employer sponsored cover.
We are a unique team of experts with specialization in MYOB, Xero Silver Champion & Advisors, and QB Pro Advisors.
- 3rd Floor 207 Regent Street, London, W1B 3HH.
- Phone: +44 203 868 2860
TAX RETURN SERVICES
Join Our Newsletter Now
Be the First to Know. Sign up for our newsletter today.
© 2013-2026 Meru Accounting. All Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy
Request Call Back

Meru Accounting
First Month Bookkeeping Free !
- Free Trial for First month Bookkeeping services worth $95
- Get Monthly Financial Statement( Click here )
- Dedicated Accountant with Backup person for each Business
- Latest Infrastructure with Great IT security
( Virtual Tour to our office )

Meru Accounting
First Month Bookkeeping Free !
- Free Trial for First month Bookkeeping services worth $95
- Get Monthly Financial Statement( Click here )
- Dedicated Accountant with Backup person for each Business
- Latest Infrastructure with Great IT security
( Virtual Tour to our office ) - Tax Filing Starting at just $350 ( Federal + 1 State )
( Check pricing for Business Owners)
Error: Contact form not found.
This will close in 0 seconds
Request Call Back OnClick

Meru Accounting
First Month Bookkeeping Free !
- Free Trial for First month Bookkeeping services worth $95
- Get Monthly Financial Statement( Click here )
- Dedicated Accountant with Backup person for each Business
- Latest Infrastructure with Great IT security
( Virtual Tour to our office )

Meru Accounting
First Month Bookkeeping Free !
- Free Trial for First month Bookkeeping services worth $95
- Get Monthly Financial Statement( Click here )
- Dedicated Accountant with Backup person for each Business
- Latest Infrastructure with Great IT security
( Virtual Tour to our office ) - Tax Filing Starting at just $350 ( Federal + 1 State )
( Check pricing for Business Owners)
Error: Contact form not found.
This will close in 0 seconds
Calendly
This will close in 0 seconds
office video
This will close in 0 seconds

